Phospholipid biochemistry
Time:2024-01-04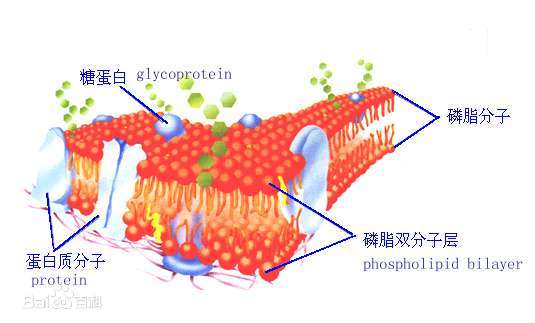
Phospholipid biochemistry refers to the study of the structure, function, metabolism, and roles of phospholipids in biological systems.Phospholipids are essential components of cell membranes and play a crucial role in various cellular processes.
Phospholipids are amphipathic molecules composed of a hydrophilic head group and two hydrophobic fatty acid tails.The structure of phospholipids contributes to their ability to form lipid bilayers, the basic structural framework of cell membranes.
Phospholipids are the major constituents of cell membranes.They form a lipid bilayer that provides a selectively permeable barrier between the cell's internal and external environments.
There are different classes of phospholipids, including phosphatidylcholine, phosphatidylethanolamine, phosphatidylserine, and phosphatidylinositol. Each class has unique properties and functions in cellular membranes.
The composition of phospholipids influences the fluidity of cell membranes.The degree of unsaturation in fatty acid chains affects membrane flexibility, which, in turn, influences various cellular processes.
Phospholipids exhibit asymmetric distribution in cell membranes.For example, phosphatidylserine is predominantly found on the inner leaflet of the plasma membrane and plays a role in cell signaling and apoptosis.
Phospholipids are involved in membrane fusion events, such as vesicle fusion during exocytosis or endocytosis.These processes are crucial for intracellular transport and communication between cells.
Cells regulate the composition of phospholipids through biosynthetic and metabolic pathways. Phospholipid metabolism involves processes like de novo synthesis, remodeling, and degradation.
Some phospholipids, such as phosphatidylinositol, serve as precursors for second messengers involved in cell signaling pathways.Phospholipid-derived molecules participate in cellular responses to various stimuli.
Proteins and mechanisms facilitate the transport of phospholipids within cells and between cellular compartments.Proper transport is essential for maintaining membrane integrity and functionality.
Phospholipids contribute to the formation of lipid rafts—microdomains within the membrane that play a role in cell signaling, membrane trafficking, and organization of membrane proteins.
Understanding phospholipid biochemistry is crucial for comprehending the fundamental processes governing cellular structure and function.Researchers in biochemistry, cell biology, and related fields study phospholipids to uncover their roles in health, disease, and various cellular phenomena.


 CN
CN





