Phospholipid biosynthesis
Time:2024-01-11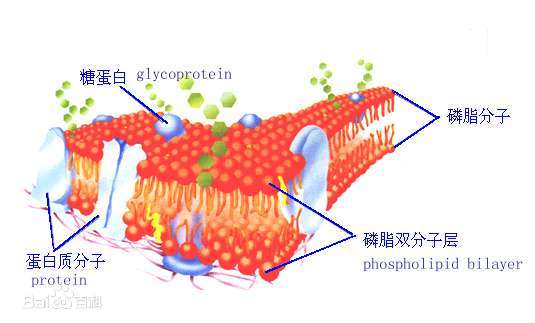
Phospholipid biosynthesis is the biological process by which cells produce phospholipids, which are essential components of cell membranes.Phospholipids have a unique structure consisting of a hydrophilic (water-attracting) head and two hydrophobic (water-repelling) tails.This structure allows phospholipids to form the lipid bilayer, the basic framework of cell membranes. The biosynthesis of phospholipids involves several steps and occurs in various cellular compartments.
The building blocks for phospholipid biosynthesis are glycerol-3-phosphate (G3P) and fatty acids. Glycerol-3-phosphate is derived from glycolysis, and fatty acids can be synthesized de novo or obtained from the diet.
1. Glycerol-3-phosphate is acylated with two fatty acids to form phosphatidic acid (PA). This step is catalyzed by the enzyme glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase.
2. Phosphatidic acid undergoes a series of enzymatic reactions to form different classes of phospholipids. For example:
Addition of a head group to PA produces phosphatidylcholine (PC), phosphatidylethanolamine (PE), phosphatidylinositol (PI), and phosphatidylserine (PS).
The specific enzymes involved in these reactions include choline/ethanolamine/inositol/serine phosphotransferases.
Remodeling and Modification: After the initial synthesis, phospholipids undergo remodeling and modification processes.Enzymes like phospholipases, acyltransferases, and methyltransferases contribute to the diversity and specificity of phospholipid species within membranes.
Subcellular Localization: Different phospholipids may be synthesized in different cellular compartments.For instance, the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a major site for phospholipid biosynthesis, but mitochondria and other organelles also contribute to the process.
Regulation: Phospholipid biosynthesis is tightly regulated to maintain membrane integrity and composition.Cellular signals, nutritional status, and environmental factors can influence the expression and activity of enzymes involved in phospholipid biosynthesis.
Transport: Phospholipids are transported to various cellular membranes, including the plasma membrane, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, and mitochondria, to fulfill specific functions.
Understanding the intricacies of phospholipid biosynthesis is crucial for grasping the fundamental processes that govern cell membrane structure and function. Dysregulation of phospholipid biosynthesis can have implications for cell membrane integrity, signal transduction, and overall cellular health.


 CN
CN





