Phospholipid function in cell membrane
Time:2023-12-21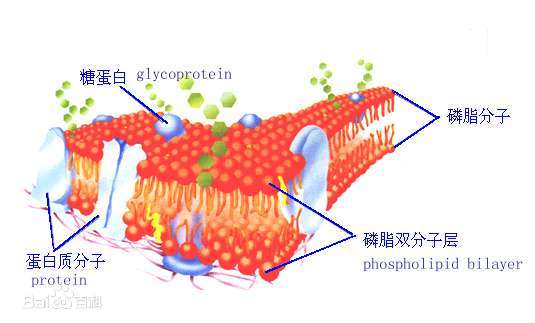
Phospholipids play a fundamental role in the structure and function of cell membranes.The cell membrane, also known as the plasma membrane, is a selectively permeable barrier that separates the internal environment of the cell from the external surroundings. Some key functions of phospholipids in cell membranes include structural foundation,selective permeability,fluidity and flexibility,embedded proteins,transport of substances,cell signaling,cell adhesion,membrane fusion and fission,membrane repair,and so on.
Phospholipids are the primary structural components of the lipid bilayer, the basic framework of the cell membrane.The lipid bilayer forms a flexible and dynamic barrier that surrounds the cell, defining its boundaries.
The arrangement of phospholipids in the lipid bilayer contributes to the selective permeability of the cell membrane.The hydrophobic tails of phospholipids face inward, creating a hydrophobic core that repels water-soluble substances while allowing the passage of lipid-soluble molecules.
Phospholipids contribute to the fluidity and flexibility of the cell membrane.The lipid bilayer is not a rigid structure; instead, it has a dynamic nature that allows for movement and interaction of molecules within the membrane.
Phospholipids serve as a matrix for the integration of proteins into the cell membrane.Proteins, including integral and peripheral proteins, are embedded or associated with the phospholipid bilayer and play crucial roles in various cellular functions such as transport, signaling, and recognition.
Certain phospholipids, such as phosphatidylcholine, can participate in the formation of specialized structures within the cell membrane, like lipid rafts.These structures may facilitate the organization of membrane proteins and play a role in the regulation of membrane transport.
Phospholipids, particularly those containing phosphate groups, are involved in cell signaling processes.For example, phosphatidylinositol phosphates (PIPs) are signaling molecules that regulate cellular processes by serving as docking sites for proteins involved in signal transduction.
Phospholipids contribute to cell adhesion by interacting with molecules on adjacent cells.This is crucial for the formation of tissues and organs, as well as for cellular interactions in processes such as immune response and embryonic development.
Phospholipids play a role in membrane fusion and fission events.During processes such as endocytosis, exocytosis, and vesicle trafficking, changes in the arrangement of phospholipids allow membranes to fuse or separate, facilitating the movement of cellular materials.
Phospholipids are involved in the repair of damaged regions of the cell membrane.Cells can reorganize and patch disruptions in the lipid bilayer, ensuring the integrity of the membrane.
In summary, phospholipids are essential components of cell membranes, contributing to the structure, flexibility, and functionality of this vital cellular barrier. Their dynamic nature allows cells to maintain integrity while responding to changes in the cellular environment and participating in various cellular processes.


 CN
CN





