Phospholipid molecular dynamics
Time:2024-01-18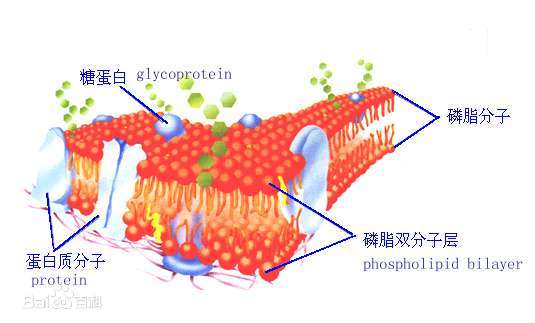
Phospholipid molecular dynamics refer to the movement and behavior of phospholipid molecules within biological membranes.The structure of phospholipids, with hydrophilic heads and hydrophobic tails, gives rise to dynamic properties that are essential for the function of cell membranes.
Phospholipids in the cell membrane are organized into a lipid bilayer.The dynamic nature of the lipid bilayer allows for flexibility, enabling the membrane to undergo various movements and deformations.
Phospholipids can undergo lateral (side-to-side) movement within the lipid bilayer.This lateral diffusion allows for the redistribution of lipids and proteins, contributing to the fluidity of the membrane.
Phospholipids can also undergo transverse diffusion, where they move from one leaflet of the lipid bilayer to the other.This process is generally slower and requires the assistance of specific enzymes or proteins.
Phospholipids can rotate around their own axes within the lipid bilayer.This rotational motion contributes to the overall flexibility and adaptability of the membrane.
The collective molecular dynamics of phospholipids determine the overall fluidity of the membrane.Membrane fluidity is crucial for various cellular processes, including the movement of membrane proteins and the regulation of membrane-bound enzymes.
Phospholipid molecular dynamics are influenced by temperature. Higher temperatures generally increase molecular motion, leading to greater membrane fluidity, while lower temperatures can reduce fluidity and increase membrane rigidity.
Phospholipid molecular dynamics play a role in cellular processes such as endocytosis, exocytosis, and vesicle formation.These dynamic movements are essential for the membrane to undergo shape changes and facilitate cellular functions.
Phospholipid dynamics are closely linked to interactions with membrane proteins.The movement of phospholipids influences the behavior of integral and peripheral membrane proteins, affecting their structure and function.
Phospholipid molecular dynamics allow the membrane to adapt to changes in the external environment.For example, cells can adjust the composition and fluidity of their membranes in response to temperature fluctuations.
Understanding phospholipid molecular dynamics is crucial for comprehending the overall behavior of cell membranes.These dynamics not only contribute to the structural integrity of the membrane but also play a vital role in facilitating various cellular processes and responses to the surrounding environment.


 CN
CN





