Phospholipid molecules in biochemistry
Time:2024-01-08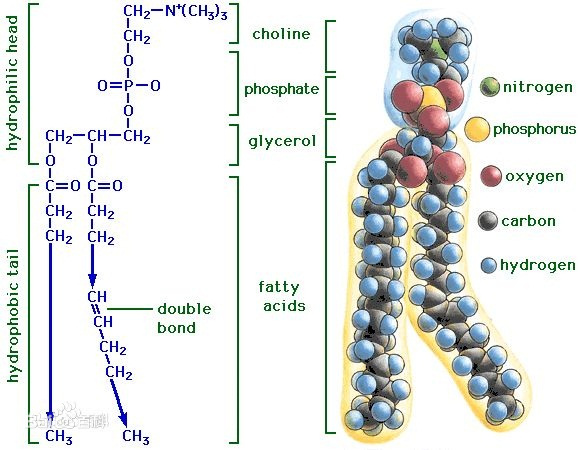
Phospholipids are crucial molecules in biochemistry, playing essential roles in the structure and function of biological membranes.These molecules consist of a hydrophilic (water-attracting) head and two hydrophobic (water-repelling) tails, creating an amphipathic structure.This amphipathic nature enables phospholipids to form the basic building blocks of cell membranes. Here are key aspects of phospholipids in biochemistry:
Cell Membrane Structure:
Phospholipids are the primary constituents of cell membranes, forming a lipid bilayer.
The hydrophilic heads of phospholipids face outward toward the aqueous environment, while the hydrophobic tails are oriented inward, creating a barrier between the inside and outside of the cell.
Types of Phospholipids:
Phosphatidylcholine, phosphatidylethanolamine, phosphatidylserine, and phosphatidylinositol are examples of common phospholipids.
Each type of phospholipid has a unique head group, influencing the properties of the lipid bilayer.
Membrane Fluidity:
The composition of phospholipids in the membrane influences membrane fluidity.
Unsaturated fatty acids in the phospholipid tails introduce kinks, making the membrane more fluid, while saturated fatty acids make it less fluid.
Function as Emulsifiers:
Phospholipids can act as emulsifiers, facilitating the dispersion of fats in water.This property is essential for digestion and absorption of dietary fats.
Signal Transduction:
Phospholipids are involved in cell signaling and signal transduction pathways.
Phosphoinositides, derivatives of phosphatidylinositol, play a role in intracellular signaling by regulating the activity of various proteins.
Lipid Rafts:
Phospholipids contribute to the formation of lipid rafts—microdomains within the membrane that contain specific lipids and proteins, influencing cellular processes.
Phospholipid Synthesis:
Cells synthesize phospholipids through various pathways, including the Kennedy pathway and the CDP-diacylglycerol pathway.
Transport Vesicles:
Phospholipids are components of transport vesicles involved in intracellular trafficking of proteins and lipids.
Energy Storage:
Phospholipids can serve as an energy store, particularly in the form of triacylglycerols (triglycerides), which consist of a glycerol backbone and three fatty acid chains.
Understanding the biochemistry of phospholipids is fundamental to grasping the structure and function of biological membranes and their role in cellular processes.Research in this area contributes to advancements in fields such as cell biology, biochemistry, and medicine.


 CN
CN





