Phospholipid properties
Time:2024-01-12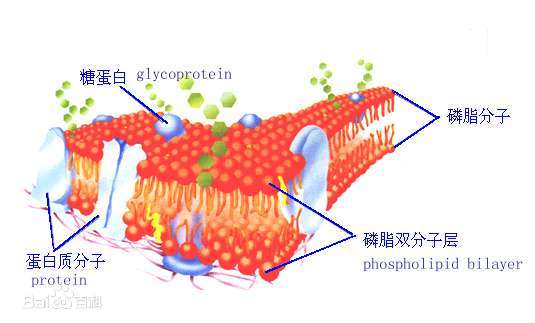
Phospholipids are essential components of cell membranes, playing a crucial role in maintaining the structural integrity and functionality of cells.
Phospholipids have a dual nature, with both hydrophilic (water-attracting) and hydrophobic (water-repelling) regions.This amphipathic property is crucial for their role in forming lipid bilayers in cell membranes.
A typical phospholipid molecule consists of a hydrophilic head and two hydrophobic tails.The head is composed of a phosphate group and glycerol, while the tails are usually fatty acid chains.The specific composition of the head group and fatty acid chains can vary among different phospholipids.
In aqueous environments, phospholipids spontaneously arrange themselves into a bilayer structure.The hydrophilic heads face outward towards the aqueous environment, while the hydrophobic tails are oriented inward, away from water.This bilayer forms the basis of cell membranes.
Phospholipids are the primary building blocks of cell membranes.The lipid bilayer provides a barrier that separates the internal environment of the cell from the external surroundings, regulating the passage of ions and molecules in and out of the cell.
The fluidity of the cell membrane is influenced by the composition of phospholipids.Saturated fatty acids in the tails tend to make the membrane more rigid, while unsaturated fatty acids introduce kinks and enhance fluidity.Cells can regulate membrane fluidity by adjusting the types of phospholipids present.
The selective permeability of cell membranes is facilitated by phospholipids.Small, non-polar molecules can pass through the lipid bilayer easily, while larger or polar molecules may require transport proteins.
Some phospholipids, such as phosphoinositides, play a role in cell signaling pathways.They are involved in the regulation of intracellular processes and the transmission of signals from the cell membrane to the cell's interior.
Phospholipids can serve as a source of energy.When broken down, the fatty acid chains release energy that the cell can use for various metabolic processes.
Cells can synthesize phospholipids through enzymatic processes.The endoplasmic reticulum is a key cellular organelle involved in the synthesis of phospholipids.
Understanding the properties of phospholipids is essential for grasping the fundamental principles of cell biology and membrane structure and function.


 CN
CN





