Phospholipid role in lipid metabolism
Time:2023-12-29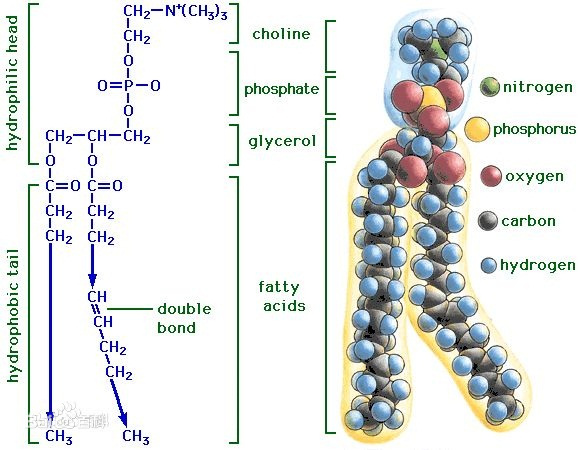
Phospholipids play a crucial role in lipid metabolism, which is the process by which the body synthesizes, breaks down, and utilizes fats (lipids).These molecules are a class of lipids that consist of a glycerol backbone, two fatty acid chains, a phosphate group, and a polar head group.The unique structure of phospholipids contributes to their significant roles in lipid metabolism.
Phospholipids are fundamental building blocks of cell membranes.They form a lipid bilayer in which the hydrophobic tails are oriented inward, while the hydrophilic heads face outward, creating a semi-permeable barrier.This structure is vital for maintaining the integrity and function of cell membranes.
Phospholipids are involved in lipid transport in the bloodstream.Lipoproteins, such as chylomicrons, very low-density lipoproteins (VLDL), low-density lipoproteins (LDL), and high-density lipoproteins (HDL), contain phospholipids as part of their structure.These lipoproteins transport lipids, including triglycerides and cholesterol, to various tissues and organs in the body.
Phospholipids aid in the emulsification of fats during digestion.In the digestive process, bile acids, which contain phospholipids, help break down large fat globules into smaller droplets, facilitating the action of lipases and enhancing the absorption of lipids in the small intestine.
Some phospholipids, such as phosphatidylinositol, function as precursors to second messengers in cell signaling pathways.Through the action of enzymes, these phospholipids can be cleaved to produce signaling molecules like inositol trisphosphate (IP3) and diacylglycerol (DAG), which are involved in various cellular responses.
While triglycerides are the primary storage form of energy in adipose tissue, phospholipids also contribute to lipid storage in cells. Phospholipids can be broken down to release fatty acids for energy production during periods of increased energy demand.
Phospholipids are involved in the regulation of lipid metabolism.For example, certain phospholipids play roles in feedback mechanisms that control the synthesis and breakdown of lipids in response to the body's energy needs.
Phospholipids are precursors for the synthesis of eicosanoids, which are signaling molecules involved in inflammation, blood clotting, and other physiological processes.Arachidonic acid, derived from certain phospholipids, serves as a precursor for various eicosanoids.
Phospholipids are multifunctional molecules that contribute to the structural integrity of cell membranes, play key roles in lipid transport, digestion, and signaling, and participate in the regulation of lipid metabolism and energy storage.Their diverse functions make them essential components in maintaining the balance and homeostasis of lipid metabolism in the body.


 CN
CN





