Phospholipid structure and function
Time:2024-01-02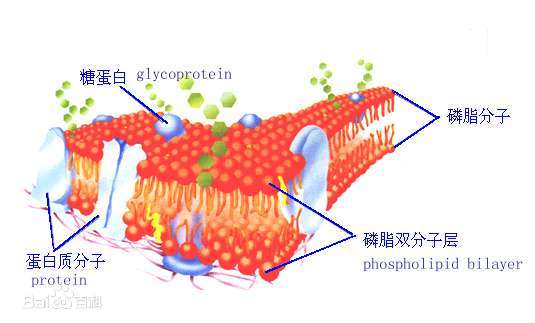
Phospholipids are a class of lipids that play crucial roles in biological membranes.These molecules have a unique structure that consists of a hydrophilic (water-attracting) head and two hydrophobic (water-repelling) tails.The structure of phospholipids is essential for their function in forming the lipid bilayer, the basic structural unit of cell membranes.Here's a breakdown of the structure and function of phospholipids:
Structure of Phospholipids:
1.Head Group:
The head group is hydrophilic and contains a phosphate group.
The phosphate group is often linked to an alcohol, such as choline, ethanolamine, serine, or inositol, forming different types of phospholipids.
2.Glycerol Backbone:
The phosphate group is linked to a glycerol molecule.
Glycerol is a three-carbon alcohol that serves as the backbone for the phospholipid.
3.Fatty Acid Tails:
The hydrophobic tails are typically composed of two fatty acid chains.
The fatty acid chains can be saturated (no double bonds between carbon atoms) or unsaturated (containing double bonds).
Function of Phospholipids:
1.Formation of Cell Membranes:
Phospholipids are the primary structural components of cell membranes.
They spontaneously form a lipid bilayer due to the amphipathic nature of their structure, with hydrophilic heads facing outward toward the aqueous environment and hydrophobic tails oriented inward away from water.
2.Cellular Compartmentalization:
Phospholipids contribute to the formation of cellular organelles and compartments, helping to define the boundaries of various cellular structures.
3.Selective Permeability:
The lipid bilayer formed by phospholipids provides a selectively permeable barrier that controls the passage of ions and molecules into and out of cells.
4.Cell Signaling:
Some phospholipids, such as phosphoinositides, act as signaling molecules in cell signaling pathways.
Phospholipids are involved in the generation of second messengers, which play a role in transmitting signals within cells.
5.Energy Storage:
Phospholipids can serve as an energy store, as they can be hydrolyzed to release fatty acids that can be used for energy production.
6.Surfactant in Lungs:
Phospholipids with specific structures, such as dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine (DPPC), are essential components of pulmonary surfactant in the lungs.This surfactant reduces surface tension, preventing the collapse of alveoli during breathing.
7.Emulsification:
Phospholipids act as emulsifiers, aiding in the dispersion of fats in water.This is important for digestion and absorption of dietary fats.
Understanding the structure and function of phospholipids is fundamental to grasping the properties of biological membranes and the diverse roles these molecules play in cellular processes.


 CN
CN





