Wholesale high-quality Phospholipids,Export from China
Time:2024-10-22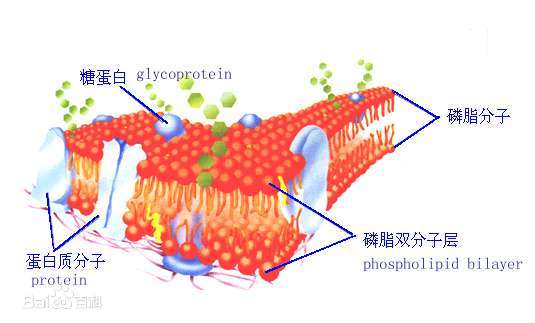
The structure of phospholipids significantly affects their solubility, primarily reflected in their amphiphilic properties. Phospholipid molecules consist of a hydrophilic phosphate group and a hydrophobic acyl chain, which results in specific solubility patterns in solvents.
Phospholipid molecules have a hydrophilic head, formed by substituent groups (such as amines or alcohols) linked by phosphate, and a hydrophobic tail made up of fatty acid chains. The hydrophilic head typically includes phosphate groups, choline, serine, etc., while the hydrophobic tail consists of long-chain fatty acids.
Solubility Characteristics of Phospholipids
·Solubility in Organic Solvents: Due to the hydrophobic region created by the acyl chains, phospholipids exhibit good solubility in organic solvents like chloroform and methanol. The molecular structures of these solvents can interact with the hydrophobic tails, facilitating dissolution.
·Solubility in Water: Phospholipids have low solubility in water because, although their hydrophilic heads can interact with water molecules, their hydrophobic tails repel water, making stable existence in water challenging. However, when the concentration of phospholipids reaches a certain level (above the critical micelle concentration, CMC), they spontaneously form bilayer vesicular structures, enhancing their stability in water.
·Influence of Acyl Chain: The solubility of phospholipids is also affected by their acyl chains. Naturally derived phospholipids generally have better solubility in alcohols compared to synthetic ones, which may relate to the unsaturation and length of acyl chains in natural phospholipids. For instance, specific phospholipids (such as PL-100M and PC-98T) can dissolve in ethanol, while DPPC cannot.
The solubility characteristics of phospholipids have important applications in various fields. In the food industry, they are commonly used as emulsifiers, antioxidants, and food shortening agents in products like margarine, baked goods, candies, and beverages. These applications leverage the emulsifying action of phospholipids at oil-water interfaces and their solubility properties in different solvents.
In summary, the structure of phospholipids significantly impacts their solubility, and their amphiphilic nature results in varying solubility patterns across different solvents, with important applications in multiple domains.


 CN
CN





